30 October 2025

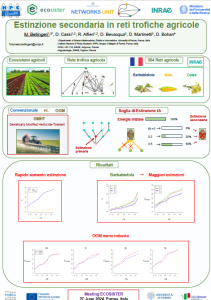
Dr Bellingeri was invited to the final event of the Ecosister project, organized by the University of Modena, to illustrate how complex network science and numerical simulation can be powerful tools for predicting the effects of biodiversity loss in agricultural ecosystems.
3 October 2025
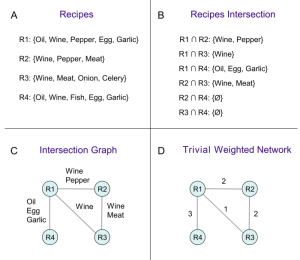
Just published: our new article that bridges network science, graph theory, computation, and data ontology to analyze and compare the structural patterns of traditional cuisine and haute cuisine.
In this study, recipes are modeled as similarity networks: nodes represent individual recipes, and links capture ingredient-based similarities between them. To quantify these relationships, we introduced a novel similarity metric—revealing how traditional and haute cuisines differ in their structural organization.
🍽️ A step forward for computational gastronomy, with exciting applications in AI, personalized recipe generation, and culinary innovation.
One key insight from the study: the interpretation of data profoundly reshapes the similarity network between recipes. Simple data mining, without critical and informed analysis, risks producing partial or misleading conclusions.
26 September 2025

Dr. Michele Bellingeri has presented “Complex Network Science for the Study of Agricultural Ecosystems” at the 21st International Conference Applied Statistics 2025, September 21–23, 2025, Koper/Capodistria, Slovenia.
7 March 2025
Dr. Michele Bellingeri has been appointed as a Guest Editor of the Research Topic article collection “Exploring Human Interactions through Sociophysics: Dynamics of Opinion Formation” of the journal Frontiers in Physics
19 February 2025
Leonardo is one of the most powerful supercomputers in Europe, located at CINECA, an Italian inter-university consortium specialized in high-performance computing (HPC).
The project will analyze the structure of real large-scale complex networks through the use of high-performance numerical simulations (high-performance computing, HPC)
20-24 January 2025
25 October 2024
21 October 2024
The article entitled ‘Machine Learning Monte Carlo Approaches and Statistical Physics Notions to Characterize Bacterial Species in Human Microbiota’ is recently published in the international journal Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction.
The research is the result of the collaboration between the Networks Unit and the Probiogenomics Laboratory of the University of Parma, directed by Prof. Marco Ventura, with the contribution of the Computational Microbiology Unit coordinated by Prof. Christian Milani ( http://probiogenomics.unipr.it/pbi/ ).
This study introduces a new approach that combines statistical physics with Monte Carlo (MC) methods to characterize bacterial species in the human microbiota at different biological ages.
Our results show that the composition of the microbiota experiences a significant transition from early childhood to adulthood.
The study shows how low-prevalence species can still play a significant role in characterizing age groups.
Finally, the research proposes a multicriteria classification of species in different age groups by integrating statistical, physical and simulation methods.
 26 July 2024
26 July 2024
Dr. Michele Bellingeri has presented “Complex Networks of Ingredients and Receipes” at the international summer course in scientific gastronomy held from July 22-26, 2024, in the Cirfood District, Reggio Emilia, Italia.
 27 June 2024
27 June 2024
The Networks Unit participated in the Conference “Ecosister in Parma: The Spoke 4 & Spoke 6”, 27 June 2024, Sala Congressi delle Scienze – Campus, Parma, with the poster “Forecasting biodiversity loss in agricultural ecological networks”
 15 June 2024
15 June 2024
The Networks Unit participated in the “WeMakeFuture” event held at the Bologna Fiere from 13 to 15 June 2024, with the poster “AI for Biodiversity”.
 17 May 2024
17 May 2024
The paper “Robustness of Real-World Networks after Weight Thresholding with Strong Link Removal”, has been published on Mathematics. This work was carried out in collaboration with the Network Science Research Group of the Indian Institute of Information Technology in Kottayam.
 16 April 2024
16 April 2024
The Network Unit participated in the poster session of the Computer Science Day 2024 held at the Mathematics building of the University of Parma.
 8 March 2024
8 March 2024
The paper “The Critical Role of Networks to Describe Disease Spreading Dynamics in Social Systems: A Perspective” has been published on Mathematics. This review underscores the critical significance of incorporating networks science in epidemiology. Classic mathematical compartmental models (CMs) employed to describe epidemic spreading may fail to capture the intricacies of real disease dynamics.
 11 December 2023
11 December 2023
Professors Cassi, Alfieri and Bellingeri, of the Network Unit of the University of Parma participated in a mission from 4 to 9 December 2023 at the laboratory of Prof. Quang Nguyen of the International University of Ho Chi Minh City. The mission is part of the project ‘Robustness and important components of real-world social weighted networks’ in the field of ICT funded by the MAECI.
 30 November 2023
30 November 2023
The paper “Random Walks-Based Node Centralities to Attack Complex Networks” has been published on Mathematics. In this manuscript, we propose four new measures of node centrality based on Random Walks (RW) and we compare the efficacy of the new RW node centralities for network dismantling with effective node removal strategies.
 11 October 2023
11 October 2023
The paper “Forecasting real-world complex networks’ robustness to node attack using network structure indexes” has been published on Frontiers in Physics. In this study, we simulate the degree and betweenness node attack over a large set of 200 real-world networks from different areas of science.
![]()
29 September 2023
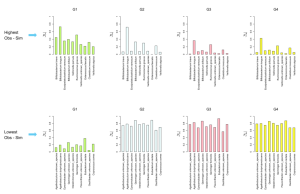
On September 29th Dr. Michele Bellengeri presented “Resilience and biodiversity loss of agricultural food webs” in the ECOSISTER Spoke6 Scientific&techincal progress workshop.
11 August 2023
The first paper resulting from the collaboration between our research group and the Network Science Research Group of the Indian Institute of Information Technology in Kottayam has been published.
22 June 2023
The Networks Unit participated at the III Conference of the Italian Society of Statistical Physics – SIFS , which was held in Parma from 21 to 23 June 2023, with the poster “Robustness and diffusion of properties in real networks”.
26 May 2023
Dr. Michele Bellingeri has been appointed as a Guest Editor of the Research Topic article collection “Compartmental Models for Social Interactions” of the journal Frontiers in Physics – section Social Physics.
28 March 2023
The paper “Considering weights in real social networks: A review” has been published on Frontiers in Physics. In this work we outline how weighted social networks (WSN) methodology may improve the modeling of several real problems in social sciences.
![]()
20 February 2023
Our network “Plant Photosystem I” (PSI) excitation energy transfer network”, has been published in the Netzschleuder repository.
The nodes represent chromophores with different identities, while edges represent FRET transfer between chromophores. The link directionality connecting nodes in the PSI network depends on the energy levels of the connected chromophores. The weights correspond to the FRET Efficiency between connected chromophores.
26 January 2023
 The paper “Effective node vaccination and containment strategies to stop the spread of the SIR epidemic in face-to-face contact networks in the real world” has been presented at the International Conference on Computing and Communication Technologies (RIVF) held in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, from 20 to 22 December 2022 and published in the conference proceedings ( doi: 10.1109/RIVF55975.2022.10013812).
The paper “Effective node vaccination and containment strategies to stop the spread of the SIR epidemic in face-to-face contact networks in the real world” has been presented at the International Conference on Computing and Communication Technologies (RIVF) held in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, from 20 to 22 December 2022 and published in the conference proceedings ( doi: 10.1109/RIVF55975.2022.10013812).
The effectiveness of the use of face mask and vaccination policies to curb the spread of the COVID-19 epidemic was evaluated by SIR simulations in four real face-to-face contact networks. This work has been realized within the “Progetto di Grande Rilevanza” collaboration, funded by MAECI.
![]()
14 December 2022
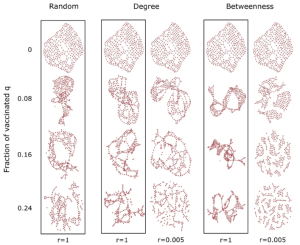 A new study by the Networks Unit entitled “A comparison of node vaccination strategies to halt SIR epidemic spreading in real-world complex networks” has been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
A new study by the Networks Unit entitled “A comparison of node vaccination strategies to halt SIR epidemic spreading in real-world complex networks” has been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
In this study we analyze the effectiveness of different vaccination strategies to curb the epidemic spread in social networks.
The results of this study are the result of our unit’s effort to setup useful tools to slow down or stop epidemics, such as the recent case of Covid 19.
The research was carried out in international collaboration with the John von Neumann Institute of Ho Chi Minh (Vietnam), and the University of Duy Tan located in the city of Da Nang (Vietnam), within the project ‘Robustness and key components of social networks with weighted links’ financed with the contribution of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation (MAECI) for the “Progetti di grande rilevanza Italia-Vietnam” in the field of ‘Information and Communication Technologies.
3 November 2022
 The Parma Networks Unit has published the results of an extensive research on the structural factors of complex networks capable of influencing the speed of epidemic spread in real networks.
The Parma Networks Unit has published the results of an extensive research on the structural factors of complex networks capable of influencing the speed of epidemic spread in real networks.
The article entitled ‘Network structure indexes to forecast epidemic spreading in real-world complex networks’ was published in the international journal Frontiers in Physics, in the special issue ‘Epidemic Models on Networks’ dedicated to the study of epidemic spread on real networks.
This article investigates which structural indicators of complex networks are most important to consider in predicting the rate of epidemic spread in real networks.
The epidemic spread was modeled through a SIR-like dynamics and the salient features of the network were described by 40 different structural indicators. The structural indicators considered the number of links in the network, the distance between nodes, the presence of community of nodes, the difference in connectivity between nodes, and many other characteristics of fundamental importance in the science of networks.
Research shows that the speed of epidemic spread is mainly determined by the ‘average distance’ between nodes from the network, that is, by the average number of bonds that must be crossed to travel between pairs of nodes. In addition to this, the density of links in the network was found to be a factor of poor predictive power of the speed of epidemic spread.
These results indicate that to predict the rate of epidemic spread in real complex networks it is not very effective to consider the simple number of links present between the nodes of the network, but it is instead necessary to consider the structure of the network and how it affects the distance between nodes.
This is particularly important in the context of measures taken to slow down or stop epidemics in social networks, such as the recent case of Covid 19.
The research was carried out in international collaboration with the John von Neumann Institute in Ho Chi Minh (Vietnam), and the University of Duy Tan located in the city of Da Nang (Vietnam), as part of the ‘Robustness and key components of social networks with weighted ties ‘funded with the contribution of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation (MAECI) for projects of Great Relevance Italy-Vietnam in the field of’ Information and Communication Technologies.
![]()
31 December 2021
 The first year of activity of our project ‘Robustness and dynamics of real social networks with weighted links’ is completed today. The project, developed in collaboration with Ton Duc Thang University (Vietnam), has been selected by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation (MAECI) as a Project of Great Relevance and funded under the ‘Italy-Vietnam Scientific and Technological Cooperation Program for the period 2021-2023′.
The first year of activity of our project ‘Robustness and dynamics of real social networks with weighted links’ is completed today. The project, developed in collaboration with Ton Duc Thang University (Vietnam), has been selected by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation (MAECI) as a Project of Great Relevance and funded under the ‘Italy-Vietnam Scientific and Technological Cooperation Program for the period 2021-2023′.
The work produced three publications in international scientific journals over the course of 2021.
Publications:
- New Betweenness Centrality Node Attack Strategies for Real-World Complex Weighted Networks, Quang Nguyen, Hgoc-Ki,-Khanh Nguyen, Davide Cassi, Michele Bellingeri, Complexity Volume 2021, Article ID 1677445
- Modularity affects the robustness of scale-free model and real-world social networks under betweenness and degree-based node attack, Nguyen, Q., Vu, T.V., Dinh, HD. et al. . Appl Netw Sci 6, 82 (2021). Modelling the consequences of social distancing over epidemics spreading in complex social networks: from link removal analysis to Sars-Cov2 prevention
- Bellingeri M, Turchetto M., Bevacqua D., Scotognella F., Alfieri R., Nguyen Q., Cassi D. Frontiers in physics, vol. 9, pg 295 (2021)
28 December 2021
The Parma Networks Unit, in collaboration with the Milan Polytechnic and the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, publishes a detailed analysis of the complex network of energy transfers of photosystem I of the common pea plant (Pisum Sativum).
Photosystem I (or plastocyanin-ferredoxin oxidoreductase, indicated by the acronym PSI) is the second photosystem involved in the photosynthetic reactions of algae, plants and some bacteria.
PSI is an integral membrane protein complex that uses the energy of light to mediate the transfer of electrons from plastocyanin to ferredoxin.
This research, using methods from graph theory, models the PSI of the pea as a network composed of nodes / chromophores and bonds indicating the energy transfers between them, and analyzes their robustness of operation.
The research entitled “The robustness of the photosynthetic system I energy transfer complex network to targeted node attack and random node failure” is published in a international journal specialized in theory and applications of network science: the Journal of Complex Networks.
2 November 2021
The paper ‘Modularity affects the robustness of scale-free model and real-world social networks under betweenness and degree-based node attack‘ has been published on Applied Network Science.
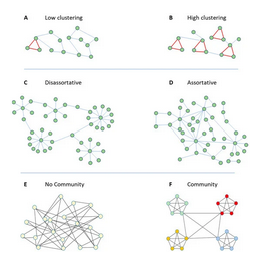
This article investigates how the modularity of networks affects their robustness to the removal of nodes.
A network with highly modularity has communities of nodes that are highly connected to nodes within the community, and poorly connected to nodes belonging to other communities.
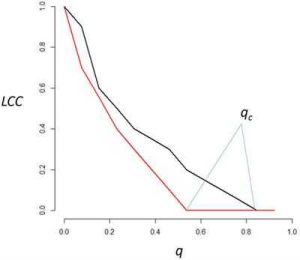
It has been discovered that highly modular networks, therefore with a marked community structure, may persent high weakness when attacked. nodes that connect different communities.
If these nodes are removed, the network is quickly fragmented thereby compromising the overall functioning of the system.
The research is included in the ‘Robustness and key components of social networks with weighted links’ project and is funded with the contribution of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation (MAECI) for projects of Great Relevance Italy-Vietnam in the field of’ Technologies of Information and Communication.
15 October 2021

The paper ‘New Betweenness Centrality Node Attack Strategies for Real-World Complex Weighted Networks’ has been published on Complexity.
The article proposes new strategies for node removal in real complex networks.
The proposed strategies proved to be very effective in identifying the most important nodes in the real complex networks analyzed in this study.
The research is included in the ‘Robustness and key components of social networks with weighted links’ project and is funded with the contribution of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation (MAECI) for projects of Great Relevance Italy-Vietnam in the field of ‘Technologies of Information and Communication’.
![]()
27 May 2021

The paper ‘Modeling the Consequences of Social Distancing Over Epidemics Spreading in Complex Social Networks: From Link Removal Analysis to SARS-CoV-2 Prevention’ has been published on Frontiers in Physics.
21 April 2021

Kick-off meeting of the international project “Robustness and important components of real-world social weighted networks” of the Networks Unit. The meeting was attended by prof. Marco Abbiati, Science Attaché at the Italian Embassy in Vietnam, and by the Vietnamese partners of the project.
![]()
12 January 2021
Two of our papers have been selected for the Complex Networks Editor’s Choice of the prestigious journal Scientific Reports:



![]()
1 July 2020
Our project “Robustness and important components of real-world social weighted networks” has been selected within the framework of the Agreement on Scientific and Technological Cooperation between the Government of the Italian Republic and the Government of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
![]()